Today, on 1st Feb, Finance Minister Srimati Nirmala Sitharaman presented the record 8th consecutive budget in the Parliament. Keeping in mind the Developed India, emphasis has been laid on agriculture, MSMEs, export, and investment, in which reform and inclusiveness have been reiterated.
In this Union Budget 2025, a special discussion was held keeping 10 major points in focus, which are as follows:
- Promoting agricultural development including productivity
- enhancing rural prosperity
- Supporting MSMEs to pave the way for employment-based economic growth
- Promoting manufacturing & Make in India
- Investing in people, economy and innovation
- Export promotion
- Nurturing innovation
- Inclusive growth
- Ensuring energy supply
- Financial sector reforms
Let us take a look at the items included in the budget which have become cheaper and costlier:
| CHEAP ITEMS | EXPENSIVE GOODS |
| Electronic items ( 5% reduction in custom duty) | TV Displays |
| Medicines (Reduction in custom duty on medicines) | Flat panel displays (Basic customs duty increased from 10% to 20%) |
| 36 lifesaving drugs | Knitted fabrics |
| Cancer drugs | |
| Medical Equipments | |
| Electric vehicles (Exemption from custom duty on 35 more items related to EVs) | |
| Mobile phones | |
| Batteries and Mineral Based Products | |
| Fish paste (Basic customs duty on frozen fish paste reduced from 30 % to 5 %) | |
| Leather goods (Exemption from basic customs duty on wet blue leather) | |
| LCD & LED TVs | |
| Clothes made in India (tax exemption) | |
| Reduction in the price of commercial cylendar (The price has decreased by ₹7 to ₹1797) |
Budget 2025 allocations

Budget 2025 allocations are strategically divided among key sectors as below-
Support to States for Infrastructure: With an outlay of ₹ 1.5 lakh crore, 50-year interest-free loans to states for capital expenditure and incentives for reforms.
Jal Jeevan Mission: To achieve 100 % coverage, the mission extended till 2028 with an enhanced total outlay.
Power Sector Reforms: Incentivize distribution reforms and augmentation of intra-state transmission. Additional borrowing of 0.5 % of GSDP to states, contingent on these reforms.
Urban Challenge Fund: ₹ 1 lakh crore to implement the proposals for ‘Cities as Growth Hubs’, ‘Creative Redevelopment of Cities’, and ‘Water and Sanitation’.
Maritime Development Fund: with a corpus of ₹25,000 crore for long-term financing with up to 49 % contribution by the government.
Nuclear Energy Mission for Viksit Bharat: Amendments to the Atomic Energy Act and the Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act will be taken up for active partnership with the private sector.
UDAN: Regional connectivity to 120 new destinations and carry 4 crore passengers in the next 10 years.
Future needs of Bihar: Greenfield airports, Financial support for the Western Koshi Canal ERM Projects.
SWAMIH Fund-2: ₹ 15,000 crore for expeditious completion of one lakh dwelling units through blended finance.
Research, Development & Innovation Allocation: ₹ 20,000 crore to implement private sector-driven
Research, Development, and Innovation initiative.
PM Research Fellowship: To provide ten thousand fellowships for technological research in IITs and IISc.
Gene Bank for Crops: Germplasm The 2nd Gene Bank with 10 lakh germplasm lines to be set up for future food and nutritional security.
Gyan Bharatam Mission: Documentation and conservation of our manuscript heritage to cover more than 1 crore manuscripts. National Digital Repository of Indian knowledge systems for knowledge sharing to be set up.
National Geospatial Mission: To develop foundational geospatial infrastructure and data. Using PM Gati Shakti, facilitation of modernization of land records, urban planning, and design of infrastructure projects.
Export Promotion Mission: With sectoral and ministerial targets to facilitate easy access to export credit, cross-border factoring support, and support to MSMEs to tackle non-tariff measures in overseas markets.
BharatTradeNet: A digital public infrastructure, ‘BharatTradeNet’ (BTN) for international trade will be set up as a unified platform for trade documentation and financing solutions. Support for integration with Global Supply Chains.
National Framework for GCC: As guidance to states for promoting Global Capability Centres in emerging tier 2 cities.
Warehousing facility for air cargo: To facilitate the upgradation of infrastructure and warehousing for air cargo including high-value perishable horticulture produce.
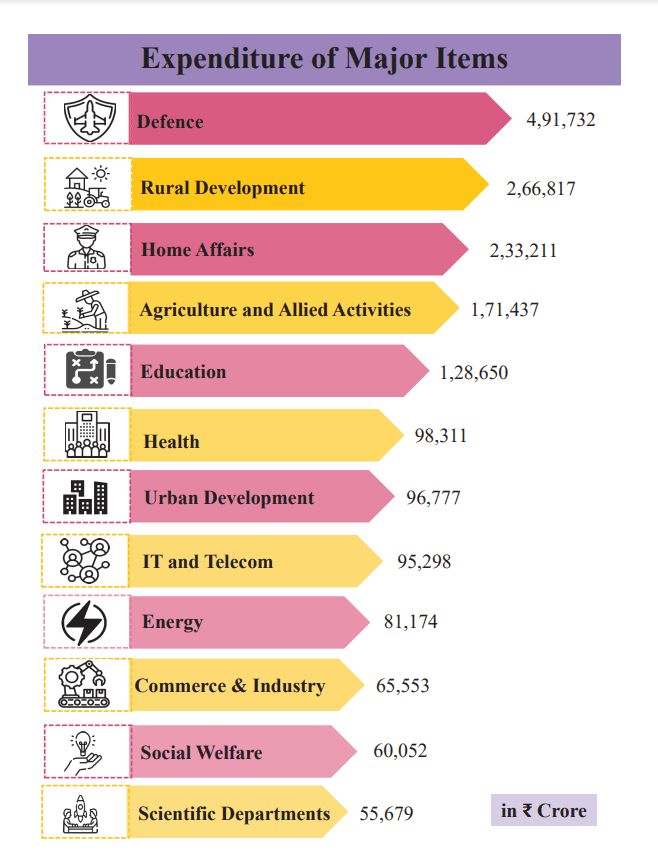
Ministry allocation
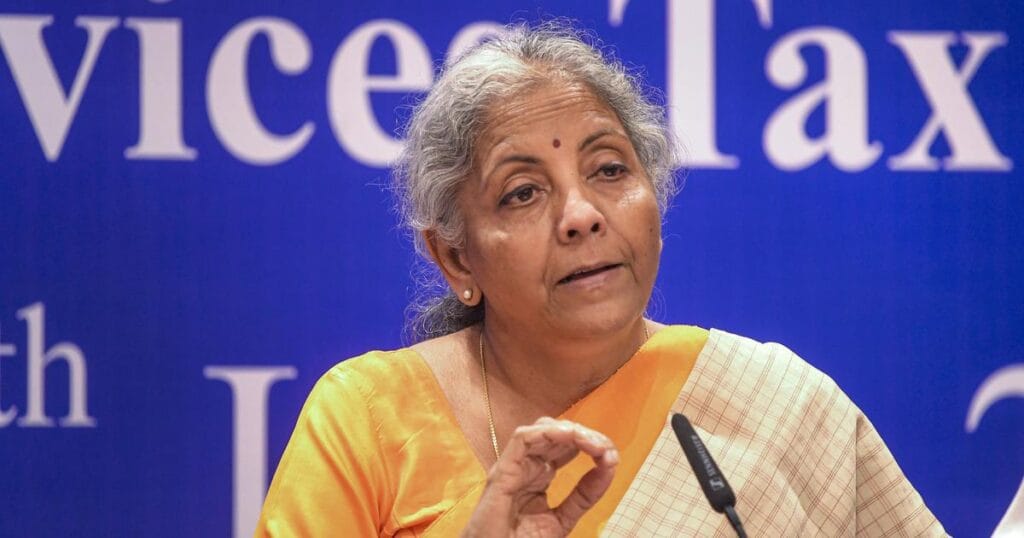
In Budget 2025, the Defense Ministry is getting the biggest allocation of close to 5lac crore. For more details of Budget 2025, click here